Foil air bearing design and installation guide
Foil Thrust Air Bearing
Mounting and Prep
Clean base plate, housing, bearing, runner (thrust disc), and fasteners with isopropyl alcohol only. Do not lubricate. Align the four pin-slots on the bearing with precision dowel pins in the base plate; apply a light press-fit to seat the bearing.

Axial Clearance
The shaft must pass freely through the bearing’s inner diameter (ID) without friction or binding. Set the axial clearance — the gap between the top foil and the runner surface — to 7.5 – 12.5 µm (0.00030 – 0.00050 in). Use calibrated shims or feeler gauges at several positions (e.g., 0°, 90°, 180°, 270°) to ensure uniform clearance around the runner. After shimming, verify free rotation by hand before performing break-in at low speed.



Design & Installation Guides
Orientation & Thrust Reversal
To avoid thrust reversal, use two thrust bearings—one CW + one CCW— on opposite sides of the runner when possible. Label and verify arrow direction (CW/CCW).

Base Plate
The base plate is a mounting fixture provided by the customer. Its function is to fix/locate the bearing within the bearing housing (alignment and retention). It does not belong to the shaft/rotor design and carries no rotational features. Dimensions, hole patterns, and dowel locations are application-specific and should match your housing and datum scheme.
Notes on Operation
Foil bearings are self-acting; under rotation they generate their own gas film and typically do not require external pressurization. (Retain optional purge air only if your design needs debris control or cooling.)
Axial Clearance Check
Place calibrated shims between runner and top foil; adjust hub/runner position to 7.5–12.5 µm, verifying at 0°, 90°, 180°, 270°. Tighten hub screws in a star pattern.
Orientation Check
If using dual bearings, install CW on one side and CCW on the other side of the runner; confirm arrows before closing.
Break-in Procedure Check
Rotate by hand to confirm no rub. Power up and ramp: 10% → 30% → 60% → 100% speed, holding 1–2 minutes at each step to establish the film. Listen for contact; if detected, stop and re-verify clearance/alignment.
Final QA Check
Recheck axial float at operating temp if applicable; document measured clearances.
CW and CCW directions shown below.


Foil Thrust Air Bearing Flow Dynamics
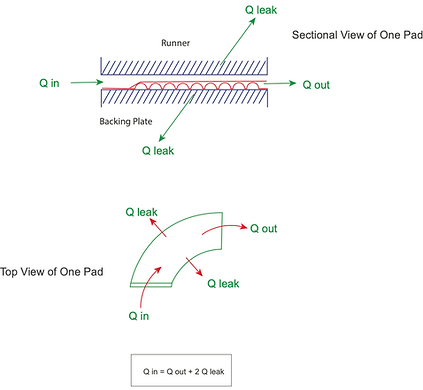
Figure 1: Foil bearings are self-acting; the hydrodynamic gas film forms with speed—no external pressurization is required for operation.
Foil Journal Air Bearing
Mounting & Prep
Use lint-free wipes + isopropyl alcohol (no oil). Seat the bearing in the housing using dowel pins/screws with a light press, or an ISO H7/g6transition fit. Slide the shaft/rotor through carefully to avoid touching the foil edges.
Radial Clearance
Target 7.5–12.5 µm radial clearance between the top foil and rotor. Verify with calibrated feeler gauges at 0°, 90°, 180°, 270°; adjust concentricity as needed.
Base Plate
The base plate is a mounting fixture provided by the customer. Its function is to fix/locate the bearing within the bearing housing (alignment and retention). It does not belong to the shaft/rotor design and carries no rotational features. Dimensions, hole patterns, and dowel locations are application-specific and should match your housing and datum scheme.





Fasten
Tighten housing screws in a cross pattern; confirm free rotation by hand.
Orientation
Match the bearing’s CW/CCW marking to your rotation direction.
Break-in Procedure Check
Ramp speeds in stages (10% → 30% → 60% → 100%), holding ~1–2 minutes at each step. Stop if any rub is detected, re-verify clearance and alignment.
Final QA Check
Measure current draw or temperature rise at rated speed to baseline performance.

CW and CCW orientation shown below.

Foil Journal Air Bearing Flow Dynamics
